Preclinical Research Projects
GABAergic Mechanisms in Schizophrenia
Miwa H, et al.
Glutamate decarboxylase 67 deficiency in a subset of GABAergic veurons induces schizophrenia-related phenotypes.
Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 2475-2486, 2015.
(Published from Gunma University)
Decreased expression of the GABA synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) in a subset of GABAergic neurons, including parvalbumin (PV)-expressing neurons, has been observed in postmortem brain studies of schizophrenics and in animal models of schizophrenia. However, it is unclear whether and how the perturbations of GAD67-mediated GABA synthesis and signaling contribute to the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. To address this issue, we generated the mice lacking GAD67 primarily in PV neurons and characterized them with focus on schizophrenia-related parameters.
Neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia
Furuie H and Yamada M
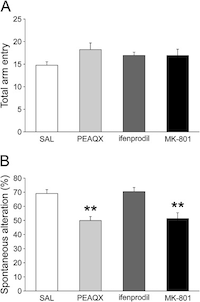
Neonatal blockade of NR2A-containing but not NR2B-containing NMDA receptor induces spatial working memory deficits in adult rats.
Neuroscie Res, in press, 2021.
The immature brain is highly sensitive to disturbances in the functioning of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in rodents, and blockade of the receptor during postnatal brain development period causes schizophrenia-like behavior in adulthood. During the postnatal period, NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors are highly expressed, and these two subunits show different expression patterns in the brain. However, the functions of these two NMDA receptors are unknown. In this study, we treated rats with an NR2A-preferring NMDA receptor antagonist (PEAQX, 10 mg/kg), an NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist (ifenprodil, 7.5 mg/kg), or a nonselective blocker of the NMDA receptor (MK-801, 0.4 mg/kg) during the neonatal period. Rats neonatally treated with MK-801 or PEAQX showed spatial working memory deficits in the Y-maze test. PEAQX-treated rats also showed greater reactivity to acoustic stimuli and hypersensitivity to acute MK-801 challenge. However, ifenprodil treatment did not cause any detectable behavioral changes. These results suggest that the NR2A-containing NMDA receptor is indispensable for proper brain development in rats, and functional disturbances in this subunit impair hippocampus-dependent spatial working memory in adulthood.
The roles of the orbitofrontal Cortex in the pathophisiology of psychiatric disorders.
Optogenetic and chemogenetic approaches.
Kuniishi H, et al.
Stress induces insertion of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in the OFC–BLA synapse and modulates emotional behaviours in mice.
Translational Psychiatry 10: 154, 2020.
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is involved in emotional processing, and orbitofrontal abnormalities have often been observed in various affective disorders. Thus, chronic dysfunction of the OFC may cause symptoms of affective disorders, such as anxiety, depression and impulsivity. Previous studies have investigated the effect of orbitofrontal dysfunction on anxiety-like behavior and impulsive aggression in rodents, but the results are inconsistent possibly reflecting different methods of OFC inactivation. Therefore, we are currently investigating the roles of the OFC in the pathophisiology of psychiatric disorders using optogenetic and chemogenetic approaches.
Chronic social defeat stress model focusing on the psychological stress:
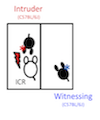
The social defeat witness model
Nakatake Y, et al.
The effects of emotional stress are not identical to those of physical stress in mouse model of social defeat stress.
Neurosci Res in press, 2020. (Available online 16 October 2019)
Chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) models in rodents are often used for researches on stress-related psychiatric disorders. CSDS includes emotional and physical aspects of stress and it is difficult to distinguish these two components. However, in many cases, patients are affected solely by emotional rather than physical distress. Recently, we have established a new stress model focusing on the emotional stress using witnessing the defeat of a conspecific. In this study, we examined the effect of emotional stress on the behavior and the plasma cytokine levels in mice.
Pharmacological intervention to regulate the extinction and reconsolidation of fear memory
Akagi K, et al.
Post-reexposure administration of riluzole attenuates the reconsolidation of conditioned fear memory in rats.
Neuropharmacol 131, 1-10, 2018.
Recently, we demonstrated that riluzole, which has been shown to block the glutamatergic system, facilitates fear extinction in rats. Here, we undertook experiments on contextual fear conditioning to clarify the actions of riluzole on the reconsolidation of fear memory in rats. We demonstrated that riluzole impaired the reconsolidation of contextual fear memory. Results from spontaneous recovery experiments also suggested that riluzole attenuated reconsolidation. Indeed, conditioned fear did not recover spontaneously 4 weeks after a short reexposure and riluzole administration, whereas it recovered after a long reexposure. Using western blotting, we demonstrated that a short reexposure increased the phosphorylation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein significantly in the dorsal part of hippocampus. Interestingly, this phosphorylation was attenuated by riluzole with short reexposure. In addition, bilateral microinjection of riluzole directly into the dorsal hippocampus clearly attenuated the reconsolidation. These findings suggested that the attenuating effect of riluzole on the reconsolidation of fear memory involves, at least in part, the dorsal part of the hippocampus.