| ON THE COVER | 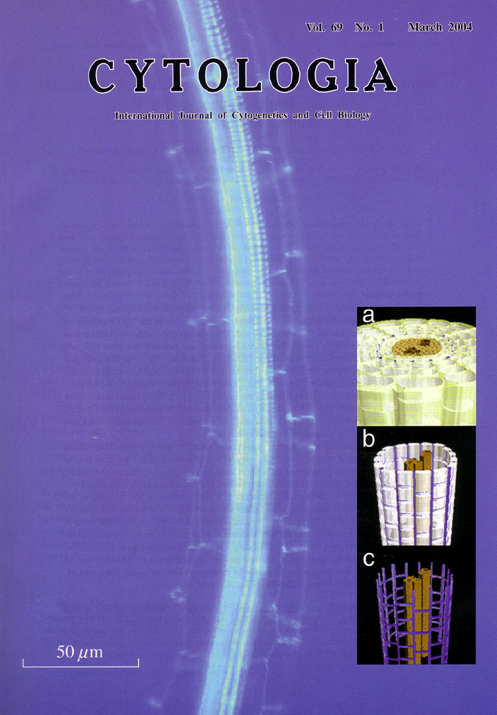 |
|---|---|
| Vol. 69 No.1 Murch 2004 | |
| Technical note | |
|
|
|
| The Casparian strip visualized
by clearing of a hypocotyl of Arabidopsis.The
hypocotyl of a 4-day-old Arabidopsis seedling grown in the light was fixed in FAA (3.7% formaldehyde, 5% acetic acid and 50% ethanol)
and clarified by treatment in 10% (w/v) KOH (l05°C,1min). The cleared hypocotyl was mounted on a
glass slide and observed under fluorescence microscope (BX-FLA; Olympus; Tokyo, Japan)
equipped with a filter assembly for excitation by ultraviolet
(UV) light (U-MWU: excitation filter,BP330-385; dichroic mirror, DM-400). The Casparian strip and xylem vessels
emit auto-fluorescence under UV light because they are
impregnated with lignin (main panel). Inset panels (a-c) illustrate digital
3-dimensional models showing the structure of the Casparian strip in a
hypocotyl. a) Tissue organization of a hypocotyl. b) The endodermis and xylem
vessels. c) The Casparian strip and xylem vessels. The Casparian strip is the barrier to apoplastic transport that is located in the radial walls of endodermal cells in roots and shoots of vascular plants. The Casparian strip is formed by individual endodermal cells but it must be continuous to function. Actually, the Casparian strip encircles each endodermal cell and is continuous throughout the entire endodermal tissue (main panel). However, it is totally unknown how the precise deposition of the strip is regulated, what signals are responsible for this very localized deposition, and how each unit is precisely located adjacent to the next. As an initial attempt to define these mechanisms, the authors assumed that there might be some positional information indicating the future site of the strip and obtained morphological evidence for the existence, prior to lignification, of some positional information in the radial wall of endodermal cells that defines the future site of formation of the strip (see Yokoyama M. and Karahara I. 2001 : Planta, 213: 474-477). (Yoshihiro Homma and Ichirou Karahara, Department of Biology; Faculty of Science, Toyama University, 3190 Gofuku, Toyama, Toyama, 930-8555, Japan) |
|