| ON THE COVER | 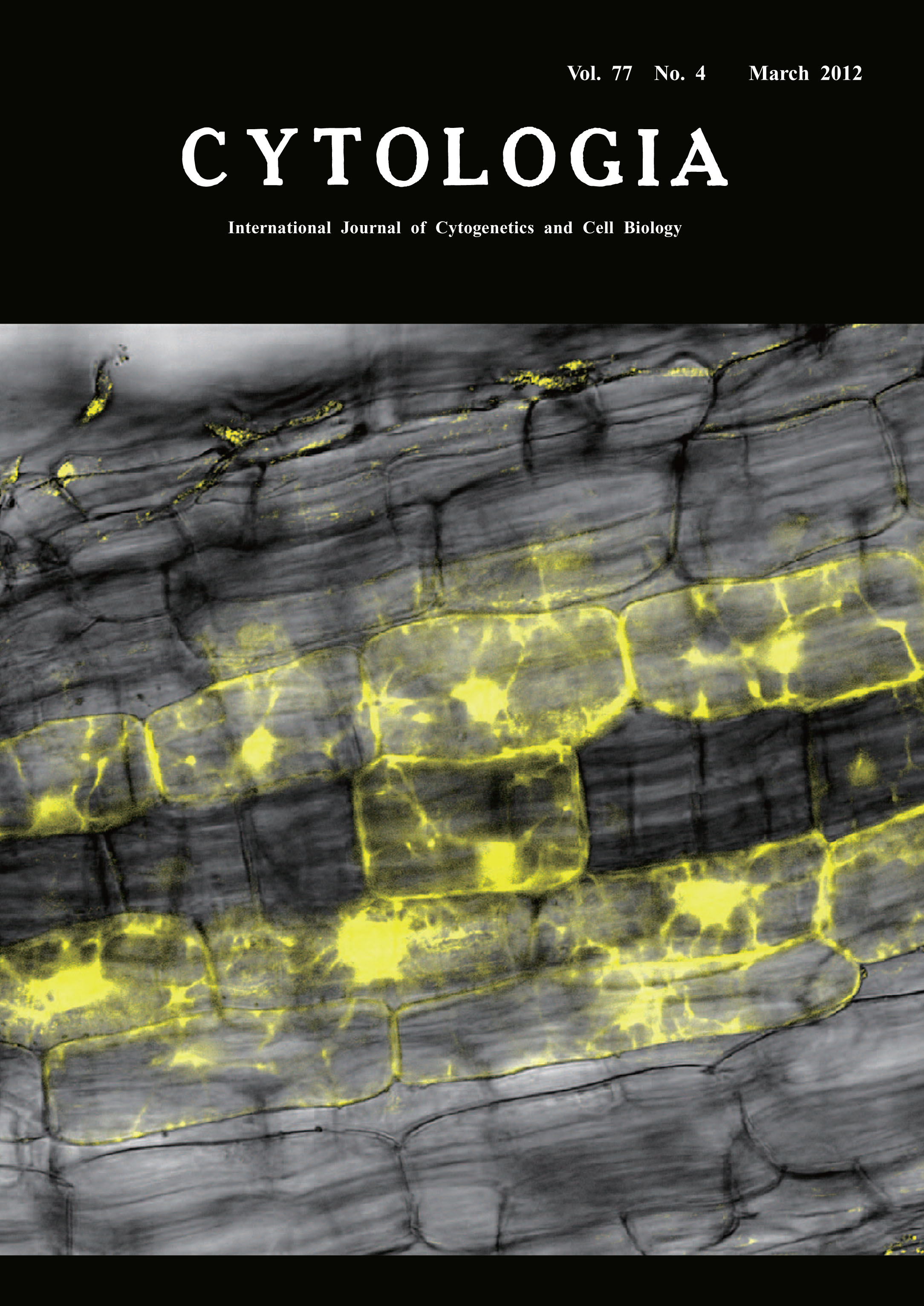 |
|---|---|
| Vol. 77 No.4 December 2012 | |
| Technical note | |
|
|
|
| Cytological Changes in Root Cortex Induced by Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Fungi Arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) fungi are obligatory symbionts of plants. More than 70% of land plants establish symbiosis with AM fungi, in which inorganic nutrients and water are supplied to host plants through external hyphae of the fungi. This symbiosis requires a set of plant proteins for function, e.g. subtilisin-like serine protease SbtM1 and calcium and calmodulin dependent protein kinase CCaMK. Upon infection of AM fungi, an intracellular structure called the pre-penetration apparatus (PPA) is formed prior to invasion of the fungi. This accompanies massive re-organization of cytoplasmic structures, including rearrangement of ER and microtubules, and migration of the cell nuclei. It is postulated that formation of the PPA facilitates fungal penetration into the host cells. The picture shows the PPA structure induced by gain-of-function CCaMK, without presence of AM fungi. Yellow fluorescence is presented by expression of Venus driven by SbtM1 promoter. The fluorescence was detected with a confocal laser scanning microscopy (Nikon A1) equipped with a 20X objective lens. The image was acquired and analyzed using the NIS elements (Nikon). See article by Takeda, N., Maekawa, T. and Hayashi, M. 2012. Plant Cell 24: 810-822. (Makoto Hayashi, Plant Symbiosis Research Unit, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305?8602, Japan) |
|