| ON THE COVER | 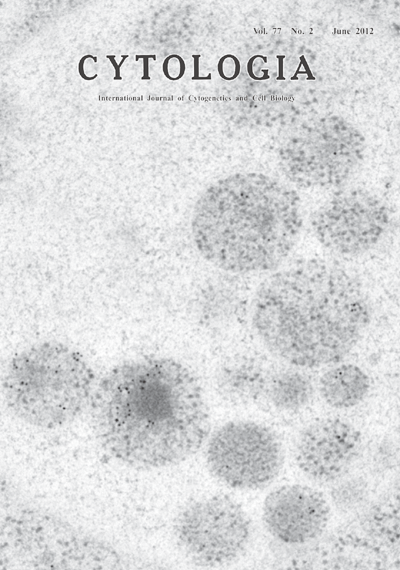 |
|---|---|
| Vol. 77 No.2 June 2012 | |
| Technical note | |
|
|
|
| Retrotransposition is Downregulated by Selective Autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Macroautophagy (autophagy) is a bulk degradation system of cytoplasmic components conserved in eukaryotic cells. Autophagy can be induced by starvation and plays a cytoprotective role by degrading unwanted cytoplasmic materials. The Ty1 transposon, a member of the Ty1/copia superfamily, is the most abundant retrotransposon in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutations can be introduced into the host genome via Ty1 virus-like particles (VLPs) in the cytoplasm. Upon starvation, Ty1 VLPs are selectively enclosed by the autophagosome. In vacuolar proteinase-deficient cells (pep4Δ), the inner membrane structures of autophagosomes (autophagic bodies), are observable as highly mobile particles inside the vacuole by light microscopy. Picture displayed is an electron microscopic image of the autophagic bodies accumulating in the vacuole of a pep4Δ cell. Autophagy-induced cells were harvested by centrifugation and the medium was removed by aspiration. The pellets were sandwiched with copper grids and rapidly frozen in liquid propane using Leica EM CPC. The cells were freeze-substituted in acetone containing 1% distilled water. Samples were embedded in LR White resin. Anti-Ty1 Gag antibodies (Diagenode anti-Ty1-tag) were used to detect Ty1 VLPs. Immunogold signals of Ty1 VLPs are localized in autophagic bodies. The diameters of autophagic bodies are ranged from 0.3–0.4 μm. See article by Suzuki, K., Morimoto, M., Kondo, C. and Ohsumi, Y. (2011) Dev. Cell. 21: 358–365. (Kuninori Suzuki 1 and Yoshinori Ohsumi 2 , 1 Bioimaging Center, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, University of Tokyo, FSB-101, 5–1–5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba 277–8562, Japan. 2 Frontier Research Center, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-S2-12 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 226–8503, Japan) |
|