| ON THE COVER | 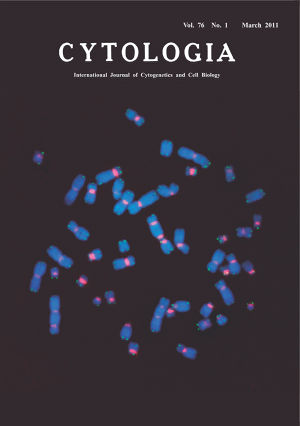 |
|---|---|
| Vol. 76 No.1 March 2011 | |
| Technical note | |
|
|
|
| Unequivocal Detection of Radiation-Induced Multicentric Chromosomes by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Using Peptide Nucleic Acid Probes Radiation exposure causes DNA strand breaks that lead to chromosomal aberrations. Among radiation-induced chromosomal aberrations, multicentric chromosomes, as represented by dicentric chromosomes (dicentrics), are considered to be sensitive and specific biomarkers for assessing radiation dose. Although the dicentric chromosome assay has for long been regarded as the “gold standard” of dosimetry, technical problems still remain in determining such chromosomal aberrations when conventionally stained metaphase chromosomes show unclear primary constrictions at their centromeric regions. Efforts have been made to precisely localize centromeres by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using pan-centromeric peptide nucleic acid (PNA) probes, which bind to the target centromeric DNA sequences quickly. We analyzed radiation-induced chromosomal aberrations by our modified technique that is simpler than the standard PNAFISH protocol (see e.g. Fomina et al., 2000). Human peripheral blood samples were exposed in vitro to gamma-rays at a dose of 5 Gy and cultured for 48 h. Chromosomal preparations were dried in an oven for 3 h at 64°C, denatured in 70% formamide/2×SSC at 70°C for 2 min and immersed in cold ethanol series. Together with a Cy3-conjugated centromere PNA probe (Cy3-ATTCGTTGGAAACGGGA), an FAM (5'-carboxyfluorescein)-conjugated telomere probe (FAM-(CCCTAA)3) was used. These synthetic fluorophore-labeled probes were commercially available (Panagene, South Korea). A total of 30µl telomere/centormere probe mix (60% formamide in 2×SSC containing 5 ng salmon sperm DNA, 3 ng FAM-telomere probe and 3 ng Cy3-centromere probe) was denatured at 90°C for 5 min and hybridized to a denatured chromosome slide at room temperature for 1 h in dark. Then, the slide was washed twice in a post-hybridization solution (2×SSC/0.1% Tween-20) for 10 min at 57°C, air-dried, and counterstained with 4,6-diamidine-2-phenylindole (DAPI). When an FITC-conjugated PNA probe was used in place of FAM-conjugated one, hybridization signals were intensified using a secondary antibody (Alexa 488-conjugateded mouse anti-FITC antibody: Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc, USA). Under these experimental conditions, the detection efficiency of centromeric signals was 100%, while that of telomeric signals was 90–100%. As seen in the cover page, three dicentric chromosomes and three acentric fragments could be detected. Each of these fragments showed telomeric signals in both termini, indicating that the fragments were formed by the fusion of two terminally deleted chromosomal materials. (Yumiko Suto, Miho Akiyama, Yuji Yamada, Research Center for Radiation Emergency Medicine, National Institute of Radiological Sciences, 4–9–1 Anagawa, Inage-ku, Chiba-shi, 263–8555, Japan) |
|