| ON THE COVER | 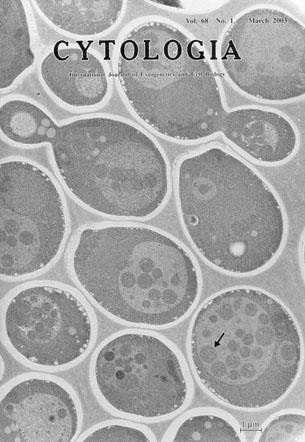 |
|---|---|
| Vol. 68 No.1 March 2003 | |
| Technical note | |
|
|
|
| Autophagy is a bulk degradation process induced
by nutrient starvation and is a complex cellular process that involves
dynamic membrane rearrangement. Upon induction of autophagy, a portion
of cytoplasm is sequestered with an isolation membrane. This results in the formation of double membrane structure called autophagosome, which subsequently delivers to a lytic compartment, the vacuole in yeast or the lysosome in mammalian cells. Herein we demonstrate that the proteinase-deficient yeast mutant had accumulated its own cytoplasmic components in the vacuoles as a form of autophagic bodies (arrow). For electron microscopic examination we used rapid freezing with propane immersion and freeze-substitution fixation method to prepare cells. The autophagic degradation is generally assumed to be nonselective and is the mechanism for turnover of organelles including mitochondria and peroxisomes. Molecular genetic studies in yeast have identified some of the components required for autophagic degradation (see reviews Ohsumi, Y.: Nature reviews, 2001. Huang W. P. and D. J. Klionsky: Cell struct. Funct., 2002). (Misuzu Baba, Yoshinori Ohsumi, Department of Cell Biology, National Institute for Basic Biology, Myodaiji, Okazaki, 444-8585, Japan) |
|